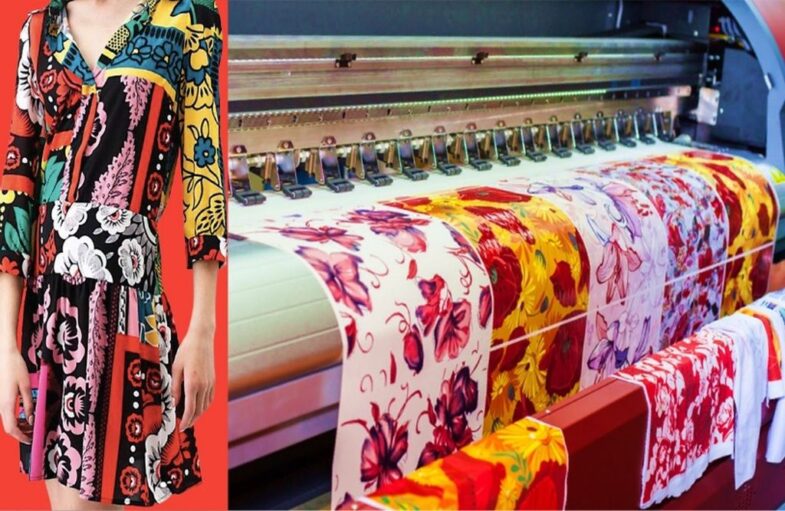
Textile printing has been around for ages, with traditional methods such as block printing, screen printing, and heat transfer dominating the industry for a long time. However, with the rise of digital technology, the textile printing industry has undergone a significant transformation. Digital fabric printing is a new and exciting technique that has become increasingly popular in recent years.
Textile printing is the process of applying designs or patterns onto fabrics using different techniques. Traditional methods such as block and screen printing involve transferring ink or dye onto fabric through a stencil or a mesh screen. These methods are time-consuming and require significant skill and expertise to produce high-quality prints.
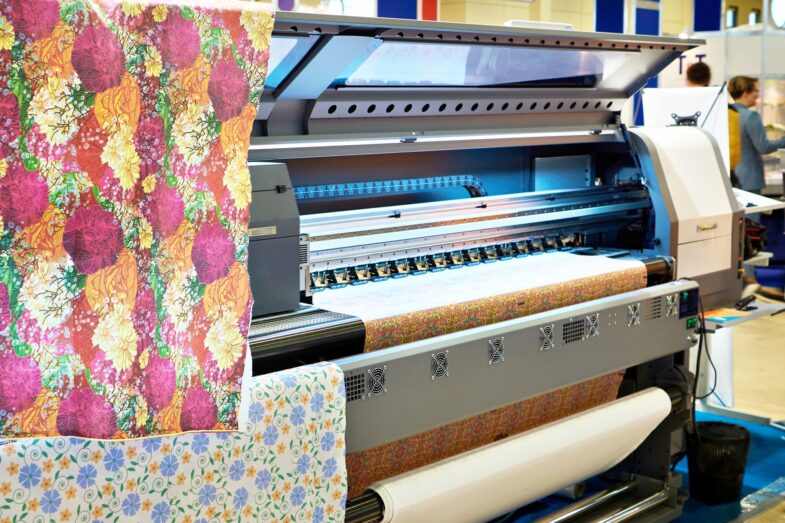
Digital fabric printing, on the other hand, is a modern printing technique that involves using digital technology to print designs directly onto fabric. It eliminates the need for intermediate steps such as stencils, screens, or rollers, resulting in a more efficient and accurate printing process.
Advantages of Digital Fabric Printing: Quality, Efficiency, and Sustainability

Source: pinterest.com
One of the main advantages of digital fabric printing is the quality of the prints. It produces high-resolution prints with sharp and vibrant colors that are fade-resistant and long-lasting. The prints are also consistent, which is important for products such as home textiles, where matching prints are crucial.
Digital printing is also more efficient than traditional methods. It eliminates the need for intermediate steps such as stencils or screens, reducing the time and cost involved in the process. The printer can produce multiple designs simultaneously, increasing productivity and reducing lead times.
Exploring the Design Possibilities
It offers endless design possibilities. It allows designers to create complex designs with intricate patterns, gradients, and textures that are difficult to achieve with traditional printing methods. Digital printing also allows for unlimited color options, making it easier to match colors to a specific brand or design.
It also enables designers to print on a range of fabrics, including natural, synthetic, and blended fabrics. This means that designers can create prints on a wider range of textiles, including delicate fabrics such as silk and chiffon.
Mass Customization: Personalizing Textile Products
Digital fabric printing is also ideal for mass customization. The technology enables manufacturers to print different designs on demand, allowing for personalized products for customers. This is particularly beneficial for the fashion industry, where customers demand unique and customized products.
Mass customization also allows manufacturers to reduce waste by producing only what is required, eliminating overproduction, and reducing the amount of unsold inventory. This can significantly reduce costs and improve profitability for manufacturers.
Sustainability: Reducing Waste and Environmental Impact

Source: freepik.com
Sustainability is a key concern in the textile industry, with increasing pressure to reduce waste and improve environmental impact. Digital technologies offer several sustainability benefits compared to traditional methods.
As mentioned earlier, it eliminates the need for water-intensive processes such as washing and steaming, which are required in traditional methods. This significantly reduces water consumption and pollution, making digital lithography a more environmentally friendly option.
It also reduces waste by producing only the required amount of fabric with minimal leftover scraps. Traditional methods often result in a significant amount of leftover fabric that is either discarded or used for less valuable products. It enables manufacturers to produce only what is required, reducing waste and improving profitability.
Furthermore, digital printing uses less energy than traditional methods, reducing the carbon footprint of textile production. This is because it only requires the amount of energy needed to print the design onto the fabric, while traditional methods require energy for several intermediate steps such as preparing screens, washing, and steaming.
Challenges and Limitations: Cost, Durability, and Complexity
One of the main challenges is the cost of digital printing. This technology is still relatively new, and the printers and inks can be expensive compared to traditional methods.
Another limitation is the durability of digital prints. While they are high-quality and vibrant, they may not be as durable as traditional prints. They may fade or wear off over time, especially with frequent washing or exposure to sunlight.
The imprinting process can also be complex and requires significant expertise and training to produce high-quality prints. The printer, ink, and fabric must be compatible and calibrated correctly to ensure accurate and consistent prints.
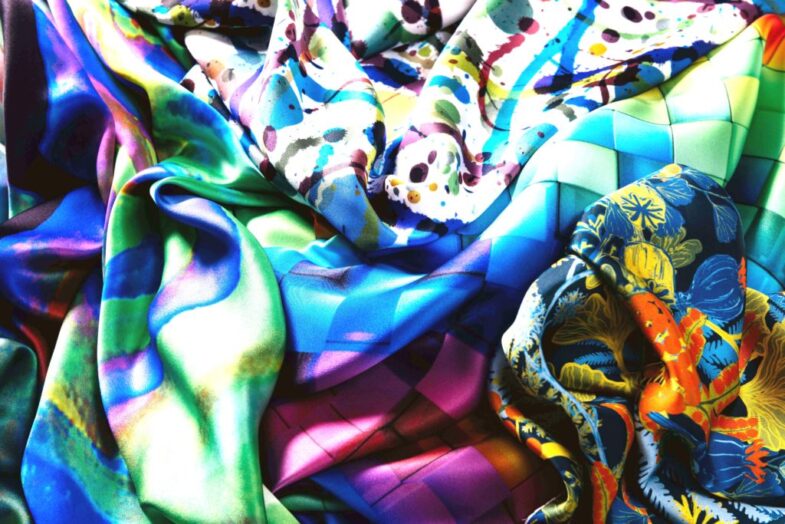
Case Studies: Successful Applications of Digital Fabric Printing in Fashion, Home Textiles, and Industrial Textiles

Source: pinterest.com
Despite the challenges and limitations, digital fabric printing has become increasingly popular in several industries. In fashion, it enables designers to create unique and personalized prints on a range of fabrics. It also allows for faster product development and reduces the time to market for new collections.
In-home textiles, this technology allows for customized and personalized products such as bedding, curtains, and tablecloths. It also enables manufacturers to produce limited runs of products, reducing waste and inventory costs.
In industrial textiles, it enables manufacturers to print complex designs onto technical textiles used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. This allows for customized and functional products with specific performance requirements.
The Future: Emerging Trends and Innovations
Digital fabric printing is a rapidly evolving technology, with several emerging trends and innovations. One trend is the use of sustainable inks and fabrics in digital printing. Manufacturers are experimenting with eco-friendly inks made from natural or renewable resources and using sustainable fabrics such as recycled polyester or organic cotton.
Another trend is the use of 3D technology in fabric engraving. 3D reproduction enables manufacturers to create complex and intricate designs with depth and texture, opening up new possibilities for textile products.
Finally, the integration of digital technology with other digital technologies such as artificial intelligence and augmented reality is another emerging trend. This allows for more personalized and interactive products that can adapt to customer preferences and behavior.
Conclusion
Overall, the future of textile printing is bright, and digital fabric printing is a key technology that will play an important role in the industry’s growth and sustainability. With its many advantages and potential applications, digital fabric printing is a technology that designers, manufacturers, and consumers should all be excited about.